Lake Trout Spawning Behavior
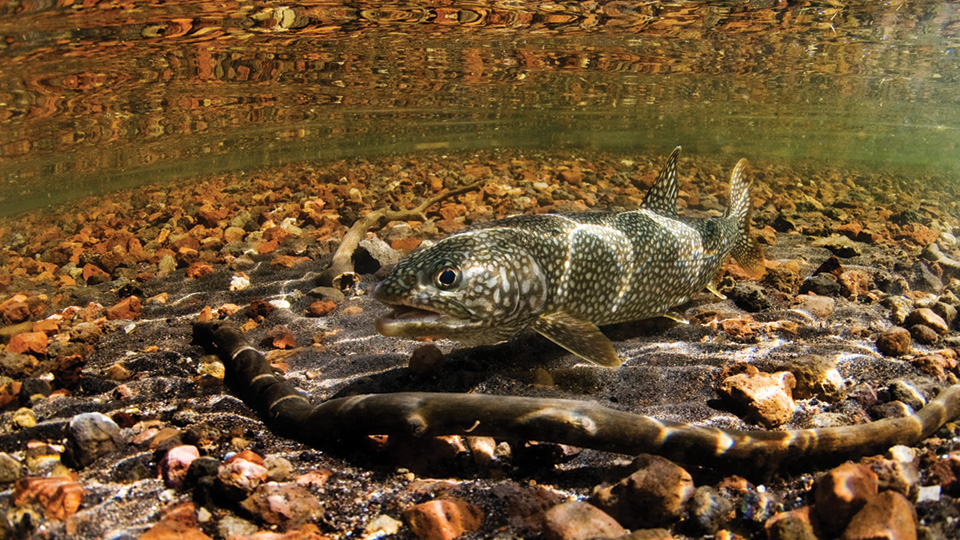
Lake trout spawning consisted of at least four distinct behaviors.
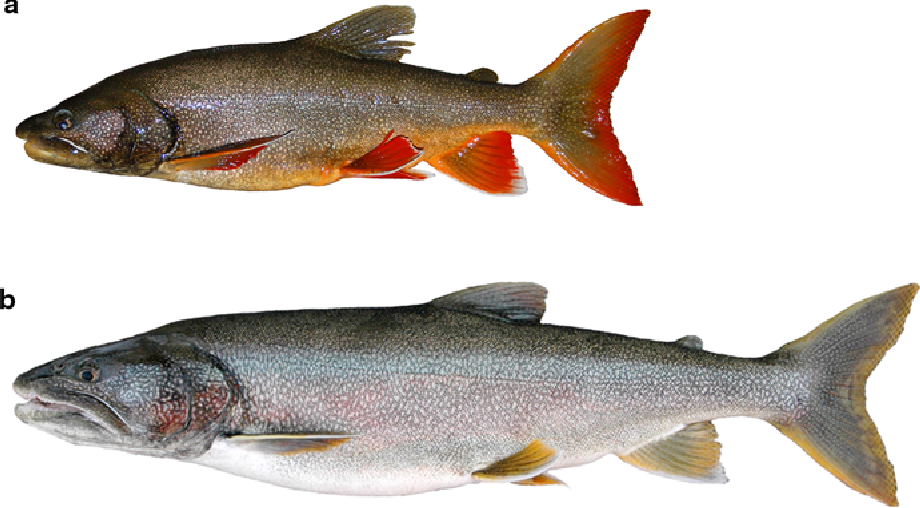
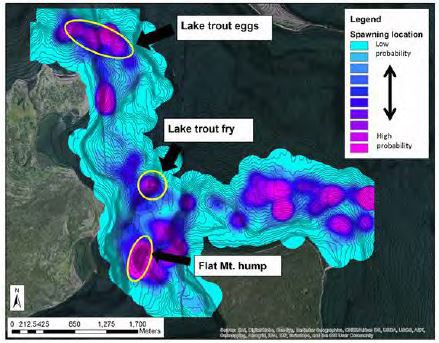
Lake trout spawning behavior. 10 m to shore in Spawning Behavior ofLake Trout 325 Social Factors in Site Selection Social cues may also play an important role in spawn- ing site selection and may in turn have contributed to the separation and maintenance of sympatric stocks ie 01-5 5-30 30. Additional spawning areas may be present at other sites near-shore or on deeper substrates. During spawning the females release their eggs and the males fertilize them externally.
Lake trout spawning consisted of at least four distinct behaviors. For example lake trout appear to be the only salmonine that 1 spawn without building a nest Martin and Olver 1980. Canadian scientists have discovered that certain lake predators are altering their behaviour due to climate change revealing what the future may hold for these fish and their food.
Courtesy of Underwater Warden Incwwwface. 2007-08-09 Lake trout spawning behaviour is described in detail and compared with other salmonine species. Hovering is a new courtship behavior that has not been previously described.
Stream-resident trout also have specific spawning requirements that relate to depth gravel size and velocity. This was taken using a VideoRay Pro 4 ROV. These observations pro-vide new insight into lake trout spawning behavior and expand the current conceptual model.
We concluded that the Bissel Point spawning area should be protected andor enhanced. Spawning lake trout are subject to predators such as bald eagles and great blue herons and their eggs were observed being consumed by carp. 2019-01-31 Brook trout spawning behavior is largely dictated by fluctuations in water temperature.
Hovering traveling sinking and gamete release. First reported direct observations of lake trout spawning in the Laurentian Great Lakes. The eggs take between four and six months to hatch.